Due diligence has emerged as a crucial concept in ensuring responsible business practices across all supply chain tiers in the textile and leather industry. This post aims to look at what it stands for and how companies approach it.
What is Due Diligence?
Due diligence is the process business enterprises should carry out to identify, prevent, mitigate, and account for actual and potential adverse impacts regarding social and environmental risks. If a risk has been identified, preventive measures must be taken to ensure that the risk does not materialise. If an adverse effect has already occurred, mitigation and remedial measures must be taken. Due to the global nature of business, due diligence applies to the company itself and along its supply chain (eg. material production, raw material processing, logistics, warehouse distribution etc.).
The idea of due diligence was adopted and endorsed by the United Nations Human Rights Council in its resolution 17/4 of June 16, 2011, in a document called the “United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs)”. This document had a formative effect on the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises. Through this process, the idea of the UNGPs was further developed and now includes human rights risks as well as environmental risks. Currently there are already due diligence legislations in place and others are in the process of being enacted.
Due Diligence Approach - Where to start?
The textile and leather industry faces increasing scrutiny regarding ethical practices and sustainability. The foundation of due diligence lies in the upstream and often also the downstream supply chain transparency, including labour rights and the environmental impact. Here is what a company should focus on to implement due diligence processes:
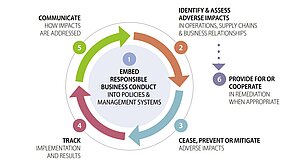
Source: OECD Guidance for responsible business conduct, page 21
Why is Due Diligence important?
Ensuring Ethical and Sustainable Practices
Due diligence allows companies to assess their suppliers, manufacturers and subcontractors to ensure they follow fair labour practices, respect human rights and meet environmental regulations.
Mitigating Risks along the Supply Chain
Companies should identify and mitigate various risks that could occur along their supply chains and ensure that suppliers and manufacturers comply with labour laws, use sustainable materials and follow ethical business practices.
Enhancing Consumer Confidence and Loyalty
Companies provide consumers with greater transparency and confidence in their products. Consumers can make informed choices, knowing that the items they purchase were produced more responsibly.
Protecting Brand Reputation
Consumers are increasingly aware of the social and environmental impact of their purchasing decisions. They expect companies to align with their values.
Laws in Europe
Up until now, the following major legislation covering the idea of due diligence are already in force:
German Supply Chain Act (LksG ), 2023: Aims to protect human rights and the environment in global supply chains and to ensure compliance with fundamental human rights and key environmental standards.
Norway’s Transparency Act, 2021: Requires companies to respect fundamental human rights and decent working conditions and ensure public access to information regarding how their negative impact is addressed.
Dutch Child Labour Due Diligence Law, 2019: Requires companies to determine if child labour occurs in their supply chains and present a plan of action to combat it.
French Duty of Vigilance Law, 2017: Requires large companies to prevent human rights violations and environmental abuse within the company itself, as well as along its supply chains.
UK Modern Slavery Act, 2015: Requires companies to disclose the steps taken to ensure that slavery and human trafficking are not present in their supply chains.
In February 2022 the European Commission proposed a Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). The Proposal is currently in the ordinary legislative process. When passed into law, the CSDDD will oblige each EU member state to adopt this directive as a bare minimum into national law. Since this Directive will be one of the most comprehensive approaches, it will greatly harmonise legal requirements regarding due diligence.
Laws in the United States
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act, 2010: Requires large retailers and manufacturers to educate consumers and provide them with information on their efforts to eradicate slavery and human trafficking from their supply chains.
New York Fashion Act, pending: Requires fashion sellers to be accountable to standardized environmental and social due diligence policies. The Act is currently under review in the New York State Senate.
Due Diligence at OEKO-TEX®
OEKO-TEX® is a solution provider for the textile and leather industry and due diligence is an important part of our modular system. It is our goal to support companies and manufacturers along their supply chains, so in 2002, we launched the management process certification OEKO-TEX® RESPONSIBLE BUSINESS - a tool to achieve responsible business conduct.
*Disclaimer: No warranty or assurance is given with respect to the completeness of the information regarding worldwide due diligence legislation.